Malware is malicious software designed to harm computer systems and is linked to data protection in several ways.
|
Malware can be used to steal or compromise sensitive data stored on a computer system or network. This data could include personal information, financial data, or confidential business information. In this sense, malware poses a significant threat to data protection, as it can lead to data breaches and other security incidents. |
|
|
Malware can be used to destroy or corrupt data, making it inaccessible or unusable. This can be particularly damaging if the data is important or essential for business operations, and can result in financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities. |
|
|
Malware can be used to exploit vulnerabilities in computer systems or networks, potentially enabling attackers to gain unauthorized access to data or systems. This can result in data theft or other malicious activities, and can also compromise the security and privacy of individuals or organizations. |
| Name | What it is | What it Does & How it infects | Examples |
 |
A type of malicious software that rapidly replicates and spreads to any device on a network. Worms do not need a host program to spread. | A worm infects a device through a downloaded file or a network connection before it multiplies and spreads at an exponential rate. |
Famous worms: Conficker, CodeRed, Morris Worm, Stuxnet |
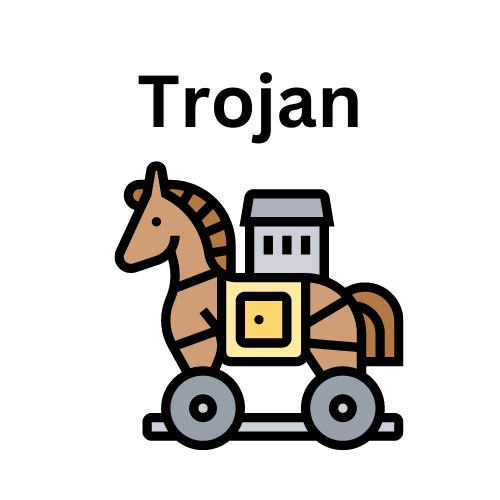 |
A trojan virus is disguised as a helpful software program. | The user downloads it, then the Trojan can gain access to sensitive data and then modify, block or delete data. It can be extremely harmful to the performance of the device. They are not designed to self-replicate, | Zeus Gameover mostly used for stealing victim's bank information. |
 |
Spyware is malicious software that runs secretly on a computer in the background and reports back to a remote user. | It targets sensitive information and can grant remote access to predators. It is often used to steal financial or personal information | Keylogger - records your keystrokes to reveal passwords and personal information. |
 |
Adware is malicious software used to collect data on your computer usage and provide appropriate adverts to you. Adware is not always dangerous but can cause issues for your system. | Adware can redirect your browser to unsafe sites and it can even contain Trojan horses and spyware. Significant levels of adware can slow down your system noticeably. |
Appearch is a common adware program that acts as a browser hijacker. It is usually bundled with free software and inserts so many ads into the browser that it makes surfing almost impossible. |
 |
Ransomware is malicious software that gains access to sensitive information within a system, encrypts that information so that the user cannot access it, and then demands a financial payout for the data to be released. | Ransomware is usually part of a phishing scam. By clicking a link the user downloads the ransomware. The attacker then proceeds to encrypt specific information that can only be unlocked with a special code. | Cryptolocker was one of the first examples. Fake Windows Updates. The VICE Society attacks schools. |
Malware is closely linked to data protection, as it poses a significant threat to the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive data. Effective measures to prevent, detect, and respond to malware attacks are essential for ensuring data protection and maintaining the security of computer systems and networks.
Check your cyber resilience using our Information and Cyber Security Checklists
Visit our Information and Cyber Security Best Practice Area for support and guidance.
In the event of a cyber attack:
Tell someone! Report to IT. Report to SLT.
Unplug the computer from the internet by removing the ethernet cable or turning the Wi-Fi off.
If you are a victim of a ransomware attack we would recommend reporting this to Action Fraud: https://www.actionfraud.police.uk/ as well as your data protection officer so they can advise about the data loss. Most cyber crimes like these will also need to be reported to the ICO by your data protection officer.
Isolate the infected device and pass to IT
Always ensure there are backups you can restore from.

